
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
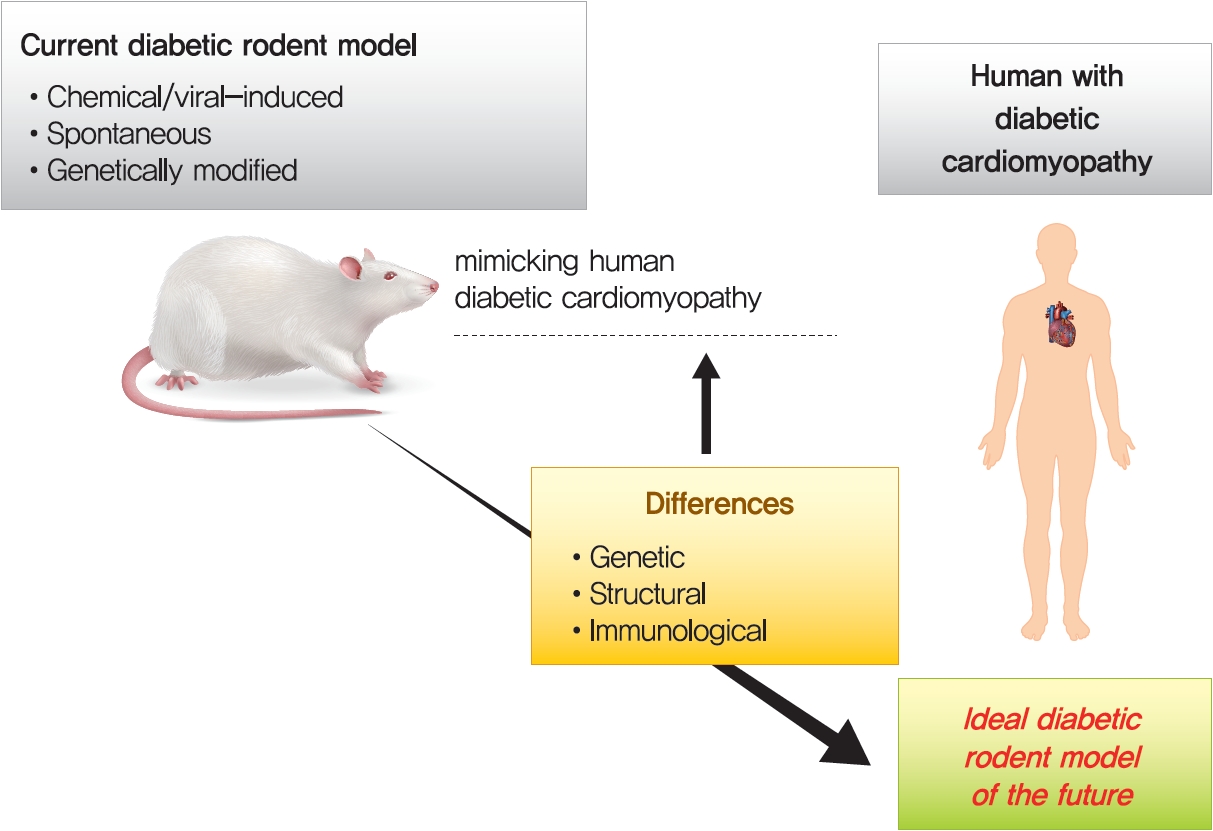
- Application of Animal Models in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- Wang-Soo Lee, Jaetaek Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):129-145. Published online March 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0285
- 9,153 View
- 332 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Diabetic heart disease is a growing and important public health risk. Apart from the risk of coronary artery disease or hypertension, diabetes mellitus (DM) is a well-known risk factor for heart failure in the form of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DiaCM). Currently, DiaCM is defined as myocardial dysfunction in patients with DM in the absence of coronary artery disease and hypertension. The underlying pathomechanism of DiaCM is partially understood, but accumulating evidence suggests that metabolic derangements, oxidative stress, increased myocardial fibrosis and hypertrophy, inflammation, enhanced apoptosis, impaired intracellular calcium handling, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, mitochondrial dysfunction, and dysregulation of microRNAs, among other factors, are involved. Numerous animal models have been used to investigate the pathomechanisms of DiaCM. Despite some limitations, animal models for DiaCM have greatly advanced our understanding of pathomechanisms and have helped in the development of successful disease management strategies. In this review, we summarize the current pathomechanisms of DiaCM and provide animal models for DiaCM according to its pathomechanisms, which may contribute to broadening our understanding of the underlying mechanisms and facilitating the identification of possible new therapeutic targets.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chitosan Versus Dapagliflozin in a Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mouse Model
Georgică Târtea, Aurel Popa-Wagner, Veronica Sfredel, Smaranda Ioana Mitran, Alexandra Oltea Dan, Anca-Maria Țucă, Alexandra Nicoleta Preda, Victor Raicea, Eugen Țieranu, Dragoș Cozma, Radu Vătășescu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2118. CrossRef - Mitochondrial energy metabolism in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Physiological adaption, pathogenesis, and therapeutic targets
Wanlin Ye, Kun Han, Maodi Xie, Sheyu Li, Guo Chen, Yanyan Wang, Tao Li
Chinese Medical Journal.2024; 137(8): 936. CrossRef - Liraglutide Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via the ILK/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling Pathway in Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Shatha M. Alobaid, Rahaf M. Alshahrani, Asma S. Alonazi, Nawal M. Alrasheed, Maha A. Alamin, Tahani K. Alshammari, Anfal F. Bin Dayel, Doaa M. Elnagar, Rana R. Alotaibi, Lama A. Almuthnabi, Dalia H. Almasud, Shahad E. Al-Ammar, Shahad O. Almadhi, Reema A.
Pharmaceuticals.2024; 17(3): 374. CrossRef - An Overview of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abdul Quaiyoom, Ranjeet Kumar
Current Diabetes Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Machine learning for spatial stratification of progressive cardiovascular dysfunction in a murine model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Andrya J. Durr, Anna S. Korol, Quincy A. Hathaway, Amina Kunovac, Andrew D. Taylor, Saira Rizwan, Mark V. Pinti, John M. Hollander, Yoshihiro Fukumoto
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(5): e0285512. CrossRef - Hyperglycemic memory in diabetic cardiomyopathy
Jiabing Zhan, Chen Chen, Dao Wen Wang, Huaping Li
Frontiers of Medicine.2022; 16(1): 25. CrossRef - Murine Models of Obesity
Tânia Martins, Catarina Castro-Ribeiro, Sílvia Lemos, Tiago Ferreira, Elisabete Nascimento-Gonçalves, Eduardo Rosa, Paula Alexandra Oliveira, Luís Miguel Antunes
Obesities.2022; 2(2): 127. CrossRef - The Role of Mitochondria in Metabolic Syndrome–Associated Cardiomyopathy
Jiayu Li, Jingye Li, Yijun Chen, Wenyu Hu, Xuhe Gong, Hui Qiu, Hui Chen, Yanguo Xin, Hongwei Li, Tao Li
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Guidelines on models of diabetic heart disease
Lisa C. Heather, Anne D. Hafstad, Ganesh V. Halade, Romain Harmancey, Kimberley M. Mellor, Paras K. Mishra, Erin E. Mulvihill, Miranda Nabben, Michinari Nakamura, Oliver J. Rider, Matthieu Ruiz, Adam R. Wende, John R. Ussher
American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology.2022; 323(1): H176. CrossRef - Extracellular vesicle therapy for non-ischemic heart failure: A systematic review of preclinical studies
Ramana Vaka, Sophie Van Remortel, Valentina Ly, Darryl R. Davis
Extracellular Vesicle.2022; 1: 100009. CrossRef - Effect of a Six-week Endurance Exercise Program and Empagliflozin Consumption on Some Structural and Functional Indices of the Heart in Male Diabetic Rats
Eftekhar Mohammadi, Mohammad Fathi, Farzaneh Chehel Cheraghi, Afshin Nazari
journal of ilam university of medical sciences.2022; 30(3): 1. CrossRef - Cardiac Phosphodiesterases Are Differentially Increased in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Rita Hanna, Wared Nour-Eldine, Youakim Saliba, Carole Dagher-Hamalian, Pia Hachem, Pamela Abou-Khalil, Delphine Mika, Audrey Varin, Magali Samia El Hayek, Laëtitia Pereira, Nassim Farès, Grégoire Vandecasteele, Aniella Abi-Gerges
Life Sciences.2021; 283: 119857. CrossRef
- Chitosan Versus Dapagliflozin in a Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mouse Model
- The Effects of Green Tea on Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- Hyun Min Kim, Jaetaek Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(3):173-175. Published online June 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.3.173
- 5,927 View
- 63 Download
- 20 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of green tea and roasted green tea on human responses
Chie Kurosaka, Chika Tagata, Sae Nakagawa, Makoto Kobayashi, Shinji Miyake
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of EGCG/tyrosol-loaded chitosan/lecithin nanoparticles on hyperglycemia and hepatic function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
Ali Es-haghi, Mozhgan Soltani, Masoud Homayouni Tabrizi, Maryam Karimi Noghondar, Niloufar Khatamian, Niloofar Barati Naeeni, Matin Kharaghani
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 267: 131496. CrossRef - The protective effect of green tea on diabetes-induced hepato-renal pathological changes: a histological and biochemical study
Tarek Atia, Hader I. Sakr, Ahmed A. Damanhory, Karim Moawad, Moustfa Alsawy
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; 129(1): 168. CrossRef - Effect of boron applications on boron concentration of the leaves under the harvest base of tea plant
Meriç Balcı, Süleyman Taban
Journal of Plant Nutrition.2023; 46(2): 184. CrossRef - Bioactive dietary components—Anti‐obesity effects related to energy metabolism and inflammation
Caroline Bertoncini‐Silva, Jean‐Marc Zingg, Priscila Giacomo Fassini, Vivian Marques Miguel Suen
BioFactors.2023; 49(2): 297. CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Effect of a Tea Mixture Nano-Formulation on Rats Occurs via the Upregulation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase/Sirtuin-1/Glucose Transporter Type 4 and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Pathways
Mohamed A. Salem, Nora M. Aborehab, Mai M. Abdelhafez, Sameh H. Ismail, Nadine W. Maurice, May A. Azzam, Saleh Alseekh, Alisdair R. Fernie, Maha M. Salama, Shahira M. Ezzat
Metabolites.2023; 13(7): 871. CrossRef - Therapeutic Properties of Green Tea: A Review
Sonia Ratnani, Sarika Malik
Journal of Multidisciplinary Applied Natural Science.2022; 2(2): 90. CrossRef - Cross-sectional associations between the types/amounts of beverages consumed and the glycemia status: The Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Diabetes study
Yusuke Kabeya, Atsushi Goto, Masayuki Kato, Yoshihiko Takahashi, Akihiro Isogawa, Yumi Matsushita, Tetsuya Mizoue, Manami Inoue, Norie Sawada, Takashi Kadowaki, Shoichiro Tsugane, Mitsuhiko Noda
Metabolism Open.2022; 14: 100185. CrossRef - The beneficial therapeutic effects of plant‐derived natural products for the treatment of sarcopenia
Mohammad Bagherniya, Atena Mahdavi, Nafiseh Shokri‐Mashhadi, Maciej Banach, Stephan Von Haehling, Thomas P. Johnston, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(6): 2772. CrossRef - Pharmaceutical Drugs and Natural Therapeutic Products for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jana Blahova, Monika Martiniakova, Martina Babikova, Veronika Kovacova, Vladimira Mondockova, Radoslav Omelka
Pharmaceuticals.2021; 14(8): 806. CrossRef - Obesity treatment by epigallocatechin‐3‐gallate−regulated bile acid signaling and its enrichedAkkermansia muciniphila
Lili Sheng, Prasant Kumar Jena, Hui‐Xin Liu, Ying Hu, Nidhi Nagar, Denise N. Bronner, Matthew L. Settles, Andreas J. Baümler, Yu‐Jui Yvonne Wan
The FASEB Journal.2018; 32(12): 6371. CrossRef - Protective effects of black tea-TV 25 on the cognitive impairments and some peripheral immune responses in intracerebroventricular colchicine injected rats
Susmita Sil, Kaushik Bhandari, Pritha Gupta, Rupsa Ghosh, Analava Mitra, Bijoy Chandra Ghosh, Tusharkanti Ghosh
Oriental Pharmacy and Experimental Medicine.2018; 18(1): 39. CrossRef - Effects of green tea extract on overweight and obese women with high levels of low density-lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C): a randomised, double-blind, and cross-over placebo-controlled clinical trial
Lin-Huang Huang, Chia-Yu Liu, Li-Yu Wang, Chien-Jung Huang, Chung-Hua Hsu
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of boron treatments on boron distribution and fresh leaf yield of tea plant
Meriç BALCI, Süleyman TABAN
International Journal of Agriculture Environment and Food Sciences.2018; 2(3): 74. CrossRef - Quercetin and Green Tea Extract Supplementation Downregulates Genes Related to Tissue Inflammatory Responses to a 12-Week High Fat-Diet in Mice
Lynn Cialdella-Kam, Sujoy Ghosh, Mary Meaney, Amy Knab, R. Shanely, David Nieman
Nutrients.2017; 9(7): 773. CrossRef - Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease: Can Tea Phytochemicals Play a Role in Prevention?
Warnakulasuriya M.A.D.B. Fernando, Geeshani Somaratne, Kathryn G. Goozee, Shehan Williams, Harjinder Singh, Ralph N. Martins
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2017; 59(2): 481. CrossRef - Hepatic transcriptome implications for palm fruit juice deterrence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in young male Nile rats
Soon-Sen Leow, Julia Bolsinger, Andrzej Pronczuk, K. C. Hayes, Ravigadevi Sambanthamurthi
Genes & Nutrition.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of high-dose green tea extract on weight reduction: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
I-Ju Chen, Chia-Yu Liu, Jung-Peng Chiu, Chung-Hua Hsu
Clinical Nutrition.2016; 35(3): 592. CrossRef - Plants and herbs for therapy of diabetes
Laurentius A. Pramono
Medical Journal of Indonesia.2015; 24(2): 67. CrossRef - Systematic Analysis of the Multiple Bioactivities of Green Tea through a Network Pharmacology Approach
Shoude Zhang, Lei Shan, Qiao Li, Xia Wang, Shiliang Li, Yuan Zhang, Jianjun Fu, Xiaofeng Liu, Honglin Li, Weidong Zhang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef
- Effects of green tea and roasted green tea on human responses
- Nutritional Status and Cardiac Autophagy
- Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(1):30-35. Published online February 15, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.1.30
- 3,568 View
- 34 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Autophagy is necessary for the degradation of long-lasting proteins and nonfunctional organelles, and is activated to promote cellular survival. However, overactivation of autophagy may deplete essential molecules and organelles responsible for cellular survival. Lifelong calorie restriction by 40% has been shown to increase the cardiac expression of autophagic markers, which suggests that it may have a cardioprotective effect by decreasing oxidative damage brought on by aging and cardiovascular diseases. Although cardiac autophagy is critical to regulating protein quality and maintaining cellular function and survival, increased or excessive autophagy may have deleterious effects on the heart under some circumstances, including pressure overload-induced heart failure. The importance of autophagy has been shown in nutrient supply and preservation of energy in times of limitation, such as ischemia. Some studies have suggested that a transition from obesity to metabolic syndrome may involve progressive changes in myocardial inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, fibrosis, apoptosis, and myocardial autophagy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Newly Proposed Mechanism of Cardiomyocyte Protection of Carvedilol-
Anti-Apoptosis Pattern of Carvedilol in Anoxia by Inducing Autophagy
Partly through the AMPK/mTOR Pathway
Jingru Li, Chaozhong Li, Guihu Sun, Longjun Li, Yongli Zeng, Huawei Wang, Xinyu Wu, Ping Yang, Yunzhu Peng, Luqiao Wang
Letters in Drug Design & Discovery.2023; 20(10): 1600. CrossRef - Mitophagy for cardioprotection
Allen Sam Titus, Eun-Ah Sung, Daniela Zablocki, Junichi Sadoshima
Basic Research in Cardiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Main active components of Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction (SMYAD) attenuate autophagy and apoptosis via the PDE5A-AKT and TLR4-NOX4 pathways in isoproterenol (ISO)-induced heart failure models
Minru Liao, Qiang Xie, Yuqian Zhao, Chengcan Yang, Congcong Lin, Guan Wang, Bo Liu, Lingjuan Zhu
Pharmacological Research.2022; 176: 106077. CrossRef - How Can Malnutrition Affect Autophagy in Chronic Heart Failure? Focus and Perspectives
Giovanni Corsetti, Evasio Pasini, Claudia Romano, Carol Chen-Scarabelli, Tiziano M. Scarabelli, Vincenzo Flati, Louis Saravolatz, Francesco S. Dioguardi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(7): 3332. CrossRef - Ischemia reperfusion injury induces pyroptosis and mediates injury in steatotic liver thorough Caspase 1 activation
Vasantha L. Kolachala, Chrissy Lopez, Ming Shen, Dmitry Shayakhmetov, Nitika Arora Gupta
Apoptosis.2021; 26(5-6): 361. CrossRef - Metformin prevents against oxidative stress-induced senescence in human periodontal ligament cells
Yunchun Kuang, Bo Hu, Ge Feng, Mingli Xiang, Yuejia Deng, Minmin Tan, Jie Li, Jinlin Song
Biogerontology.2020; 21(1): 13. CrossRef - Protective effects of salvianolic acid B against hydrogen peroxide‑induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and underlying mechanisms
Shan Gao, Shiqin Li, Qin Li, Fuyong Zhang, Mengqi Sun, Zilin Wan, Shurong Wang
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Moderate calorie restriction attenuates age‑associated alterations and improves cardiac function by increasing SIRT1 and SIRT3 expression
Wei Yu, Jinjin Qin, Chunjuan Chen, Yucai Fu, Wei Wang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiac fibrosis in the ageing heart: Contributors and mechanisms
Lu Lu, Jingbin Guo, Yue Hua, Kevin Huang, Ruth Magaye, Jake Cornell, Darren J. Kelly, Christopher Reid, Danny Liew, Yingchun Zhou, Aihua Chen, Wei Xiao, Qiang Fu, Bing Hui Wang
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology.2017; 44(S1): 55. CrossRef - MicroRNA-199a acts as a potential suppressor of cardiomyocyte autophagy through targeting Hspa5
Liang Chen, Fei-Yu Wang, Zhen-Yu Zeng, Ling Cui, Jian Shen, Xiao-Wei Song, Pan Li, Xian-Xian Zhao, Yong-Wen Qin
Oncotarget.2017; 8(38): 63825. CrossRef - Protective effects of luteolin-7-O-glucoside against starvation-induced injury through upregulation of autophagy in H9c2 Cells
Hong Yao, Lichun Zhou, Linlin Tang, Yanhui Guan, Shang Chen, Yu Zhang, Xiuzhen Han
BioScience Trends.2017; 11(5): 557. CrossRef - Hongjingtian Injection Attenuates Myocardial Oxidative Damage via Promoting Autophagy and Inhibiting Apoptosis
Shujing Zhang, Ling Zhang, Han Zhang, Guanwei Fan, Jiuwen Qiu, Zongbao Fang, Haibo Wu, Yi Wang, Xiaoping Zhao
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Autophagy is a regulator of TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis in primary human atrial myofibroblasts
S Ghavami, R H Cunnington, S Gupta, B Yeganeh, K L Filomeno, D H Freed, S Chen, T Klonisch, A J Halayko, E Ambrose, R Singal, I M C Dixon
Cell Death & Disease.2015; 6(3): e1696. CrossRef - The number of cardiac myocytes in the hypertrophic and hypotrophic left ventricle of the obese and calorie‐restricted mouse heart
Julia Schipke, Ewgenija Banmann, Sandeep Nikam, Robert Voswinckel, Karin Kohlstedt, Annemarieke E. Loot, Ingrid Fleming, Christian Mühlfeld
Journal of Anatomy.2014; 225(5): 539. CrossRef - Glycated Albumin Causes Pancreatic β-Cells Dysfunction Through Autophagy Dysfunction
Young Mi Song, Sun Ok Song, Young-Hye You, Kun-Ho Yoon, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology.2013; 154(8): 2626. CrossRef - Cardiac Metabolism and its Interactions With Contraction, Growth, and Survival of Cardiomyocytes
Stephen C. Kolwicz, Suneet Purohit, Rong Tian
Circulation Research.2013; 113(5): 603. CrossRef
- The Newly Proposed Mechanism of Cardiomyocyte Protection of Carvedilol-
Anti-Apoptosis Pattern of Carvedilol in Anoxia by Inducing Autophagy
Partly through the AMPK/mTOR Pathway
- Letter: Higher Glycated Hemoglobin Level Is Associated with Increased Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Non-Diabetic Korean Male Adults (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:551-7)
- Seok Hong Lee, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(1):79-80. Published online February 17, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.1.79
- 2,858 View
- 23 Download
- A Nationwide Survey about the Current Status of Glycemic Control and Complications in Diabetic Patients in 2006: The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus.
- Soo Lim, Dae Jung Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jeong Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Inkyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):48-57. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.48
- 2,771 View
- 55 Download
- 43 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus performed a nationwide survey about the current status of glycemic control and diabetic complications in 2006. METHODS: The current study included 5,652 diabetic patients recruited from the rosters of endocrinology clinics of 13 tertiary hospitals in Korea. Age, gender, height, weight, waist circumference and blood pressure were investigated by standard method. Fasting and postprandial 2 hour glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipid profiles, fasting insulin and c-peptide levels were measured. Microvascular (microalbuminuria, retinopathy and neuropathy) and macrovascular (coronary artery disease [CAD], cerebrovascular disease [CVD] and peripheral artery disease [PAD]) complications were reviewed in their medical records. RESULTS: Mean age of total subjects was 58.7 (+/- 11.6) years and duration of diabetes was 8.8 (0~50) years. Mean fasting and postprandial 2 hour glucose levels were 145.9 +/- 55.0 and 208.0 +/- 84.4 mg/dL, respectively. Their mean HbA1c was 7.9 +/- 1.9%: the percentage of patients within target goal of glycemic control (< 7% of HbA1c) was 36.7%. In this study, 30.3%, 38.3% and 44.6% of patients was found to have microalbuminuria, retinopathy and nephropathy, respectively. Prevalence of CAD, CVD and PAD was 8.7%, 6.7% and 3.0%, respectively. Diabetic complications were closely related with age, duration of diabetes and glycemic control, and this relationship was stronger in microvascular complications than macrovascular ones. CONCLUSION: Only about one third of patients with diabetes was found to reach target glycemic control in tertiary hospitals of Korea. More tight control is needed to reduce deleterious complications of diabetes in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of Diabetic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Dementia: A Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Claims Data
Eun Sik Jeong, Ah-Young Kim, Hye-Young Kang
Drug Targets and Therapeutics.2023; 2(1): 49. CrossRef - Prevalence of thyroid disorders in type 2 diabetic patients – A 1-year cross-sectional study
RikitaRamesh Mudhol, ShivakumarVeeranna Turamari, RekhaRamesh Mudhol, B Srinivas
BLDE University Journal of Health Sciences.2022; 7(1): 56. CrossRef - Associations of fasting glucose and glycated hemoglobin with vitamin D levels according to diabetes mellitus status in Korean adults
Yerin Hwang, Jiyoung Jang, Myung-Hee Shin
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022025. CrossRef - Atherectomy in Peripheral Artery Disease: Current and Future
Yohan Kwon, Jinoo Kim, Je-Hwan Won, Seong Ho Kim, Jeong-Eun Kim, Sung-Joon Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2021; 82(3): 551. CrossRef - Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Clinical Practice for People with Diabetes in Korea: A 10-Year Trend Analysis
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 928. CrossRef - Current status of treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ningbo, China
Tianmeng Yang, Rongjiong Zheng, Qingmei Chen, Yushan Mao
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Recently Uncontrolled Glycemia in Diabetic Patients Is Associated with the Severity of Intracranial Atherosclerosis
Nari Choi, Jeong-Yoon Lee, Jun-Sang Sunwoo, Hakjae Roh, Moo-Young Ahn, Sung-Tae Park, Kyung Bok Lee
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2017; 26(11): 2615. CrossRef - The effect of educational program based on the precede-proceed model on improving self-care behaviors in a semi-urban population with type 2 diabetes referred to health centers of Bavi, Iran
Neda Barasheh, Ghodratollah Shakerinejad, Sedigheh Nouhjah, Mohammad Hossein Haghighizadeh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2017; 11: S759. CrossRef - Increased prevalence of albuminuria in individuals with higher range of impaired fasting glucose: the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Chul Won, Jae Won Hong, Jung Min Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(1): 50. CrossRef - Assessment of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin–sulfonylurea combination: Results of a multicenter, cross‐sectional, observational study in Korea
Sin Gon Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Duk Kyu Kim, Sung Rae Cho, Dong Seop Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(3): 317. CrossRef - Current Status of Management in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in South Korea
Jin-Hee Jung, Jung-Hwa Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Jeong-Eun Park, Hee-Sook Kim, Joo-Wha Yoo, Bok-Rye Song, Jeong-rim Lee, Myeong-Hee Hong, Hyang-Mi Jang, Young Na, Hyun-Joo Lee, Jeong-Mi Lee, Yang-Gyo Kang, Sun-Young Kim, Kang-Hee Sim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 307. CrossRef - Kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1): an early biomarker for nephropathy in type II diabetic patients
Nahla E. El-Ashmawy, Enas A. El-Zamarany, Naglaa F. Khedr, Abeer I. Abd El-Fattah, Shereen A. Eltoukhy
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2015; 35(S3): 431. CrossRef - The Effect of the Experience of Diabetes Education on Knowledge, Self-Care Behavior and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Seung Hei Moon, Young Whee Lee, Ok-Kyung Ham, Soo-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 81. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Diabetic Patients Transferred to Korean Referral Hospitals
Min Young Oh, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, In Kyu Lee, Hong Sun Baek, Hyoung Woo Lee, Min Young Chung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(5): 388. CrossRef - Current Status of Prescription in Type 2 Diabetic Patients from General Hospitals in Busan
Ji Hye Suk, Chang Won Lee, Sung Pyo Son, Min Cheol Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Kwang Jae Lee, Ja Young Park, Sun Hye Shin, Min Jeong Kwon, Sang Soo Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 230. CrossRef - The Influence of Admission Hypoglycemia on Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Jung Kim, Myung Ho Jeong, In Seok Jeong, Sang Gi Oh, Sang Hyung Kim, Young keun Ahn, Ju Han Kim, Young Jo Kim, Shung Chull Chae, Taek Jong Hong, In Whan Seong, Jei Keon Chae, Chong Jin Kim, Myeong Chan Cho, Ki Bae Seung, Hyo Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Medicine.2014; 87(5): 565. CrossRef - Duration of diabetes and effectiveness of insulin in the management of insulin-naïve Korean patients uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs: a sub-analysis of the MOdaliTy of Insulin treatment eValuation (MOTIV) registry results
Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Kun Ho Yoon, Ho Young Son, Sung Woo Park, Yeon Ah Sung, Hong Sun Baek, Kyoung Soo Ha
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(4): 655. CrossRef - Is the Indicator Magnifying Window for Insulin Pens Helpful for Elderly Diabetic Patients?
Ju Hee Lee, Eun Shil Hong, Jung Hun Ohn, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 149. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Albuminuria in the Korean Adult Population: The 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Chul Won, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung Min Kim, Sang Youb Han, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim, Harald Mischak
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(12): e83273. CrossRef - The Epidemiology of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(1): 11. CrossRef - The Relationship between Neuropathic Pain and Glycemic Control, Self Management in Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Yeong-Mi Seo, Won-Hee Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1774. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study
Kee-Ho Song, Jung Min Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Yongsoo Park, Hyun-Shik Son, Kyong Wan Min, Kyung Soo Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 117. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Low ankle-brachial index is an independent predictor of poor functional outcome in acute cerebral infarction
Jinkwon Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Myoung-Jin Cha, Tae-Jin Song, Ji Hye Park, Hye Sun Lee, Chung Mo Nam, Hyo Suk Nam, Young Dae Kim, Ji Hoe Heo
Atherosclerosis.2012; 224(1): 113. CrossRef - Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Control in Korean Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes
Sun-Joo Boo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 406. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 6. CrossRef - The Association of Self-Reported Coronary Heart Disease with Diabetes Duration in Korea
Hye Mi Kang, Yun Jeong Lee, Dong-Jun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 350. CrossRef - Response: The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:543-50)
Ji Hee Yu, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 77. CrossRef - Reduction in glycated albumin can predict change in HbA1c: comparison of oral hypoglycaemic agent and insulin treatments
H. K. Won, K. J. Kim, B.‐W. Lee, E. S. Kang, B. S. Cha, H. C. Lee
Diabetic Medicine.2012; 29(1): 74. CrossRef - Management of Blood Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Survey in Korean
Mi Hae Seo, Woo Je Lee, Cheol Young Park, Sung Rae Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee, Sung Woo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 348. CrossRef - Accuracy Evaluation of the Alternative Site Blood Glucose Test Using Error Grid
Kyung-Soon Park, Eun-Jong Cha
Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research.2011; 32(1): 25. CrossRef - Glycated albumin is a useful glycation index for monitoring fluctuating and poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients
Eun Young Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Daham Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Kwang Joon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee
Acta Diabetologica.2011; 48(2): 167. CrossRef - Group Classification on Management Behavior of Diabetic Mellitus
Sung-Hong Kang, Soon-Ho Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(2): 765. CrossRef - Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soon Ae Kim, Woo Ho Shim, Eun Hae Lee, Young Mi Lee, Sun Hee Beom, Eun Sook Kim, Jeong Seon Yoo, Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 159. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Jung Hee Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 571. CrossRef - Increasing Trend in the Number of Severe Hypoglycemia Patients in Korea
Jin Taek Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Ye An Lee, Jun Ho Bae, Hyo Jeong Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Lim, Hak Chul Jang, Hong Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Rural Korea: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort Study
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Jin-Hee Lee, Man-Soo Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Won Chul Lee, Bong-Yun Cha, Ho-Young Son
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2011; 26(8): 1068. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital
Ji Hee Yu, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Mi-Seon Shin, Chang Hee Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 543. CrossRef - Prevalence, Awareness, and Control of Hypertension among Diabetic Koreans
Hyun Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 337. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Physical Activity Behavior among Iranian Women with Type 2 Diabetes Using the Extended Theory of Reasoned Action
Alireza Didarloo, Davoud Shojaeizadeh, Hassan Eftekhar Ardebili, Shamsaddin Niknami, Ebrahim Hajizadeh, Mohammad Alizadeh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 513. CrossRef - Factors that Affect Medication Adherence in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Ae Park, Jung-Guk Kim, Bo-Wan Kim, Sin Kam, Keon-Yeop Kim, Sung-Woo Ha, Sung-Taek Hyun
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(1): 55. CrossRef - The Effects of Tailored Diabetes Education on Blood Glucose Control and Self-Care
Kyung Sun Hyun, Kwang Mi Kim, Sook Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 720. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database
Ie Byung Park, Sei Hyun Baik
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(5): 357. CrossRef
- Risk of Diabetic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Dementia: A Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Tae Ho Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Soo Lim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jeong Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Inkyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):40-47. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.40
- 2,380 View
- 27 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to analyze the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: A total of 4,240 diabetic patients (male 2,033, female 2,207; mean age 58.7 +/- 11.3 years; DM duration 8.9 +/- 7.6 years) were selected from the data of endocrine clinics of 13 university hospitals in 2006. Metabolic syndrome was defined using the criteria of the American Heart Association/National Heart Lung and Blood Institute and the criteria of waist circumference from the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. RESULTS: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 77.9% (76.7% of males, 78.9% of females). The average number of the components of metabolic syndrome was 2.4 +/- 1.1. Abdominal obesity was seen in 56.8% of the patients, hypertriglyceridemia in 42.0%, low HDL cholesterol in 65.1%, and high blood pressure in 74.9%. Abdominal obesity and high blood pressure were much more prevalent among females than males, and low HDL cholesterol was much more prevalent among males than females. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was not different according to the duration of diabetes. Metabolic syndrome was strongly related with obesity (odds ratio, 6.3) and increased age (odds ratio in the over 70 group, 3.4). CONCLUSION: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 77.9% in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. Its prevalence was greater in obese patients and in those over 40 years of age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Novel Clinical Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome: Vascular Risk Age
Abdulrahman Naser, Didar Elif Akgün, Rengin Çetin Güvenç, Samet Sayılan, Özgen Şafak
Bagcilar Medical Bulletin.2023; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Risk of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Subjects with Prediabetes Overlapping Metabolic Syndrome
Seol A Jang, Kyoung Min Kim, Seok Won Park, Chul Sik Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 599. CrossRef - Metabolic Age, an Index Based on Basal Metabolic Rate, Can Predict Individuals That are High Risk of Developing Metabolic Syndrome
Sarahi Vásquez-Alvarez, Sergio K. Bustamante-Villagomez, Gabriela Vazquez-Marroquin, Leonardo M. Porchia, Ricardo Pérez-Fuentes, Enrique Torres-Rasgado, Oscar Herrera-Fomperosa, Ivette Montes-Arana, M. Elba Gonzalez-Mejia
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2021; 28(3): 263. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome among type 2 diabetic patients in Sub-Saharan African countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Wondimeneh Shibabaw Shiferaw, Tadesse Yirga Akalu, Mihretie Gedefaw, Denis Anthony, Ayelign Mengesha Kassie, Worku Misganaw Kebede, Henok Mulugeta, Getenet Dessie, Yared Asmare Aynalem
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 1403. CrossRef - Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Value Based on Insulin Resistance and Visceral Obesity in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes
Jung Soo Lim, Young Ju Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Byoung Wook Huh, Eun Jig Lee, Kap Bum Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 253. CrossRef - The Relations between Diabetic Dietary Compliance, Dietary Intake, and Physical Activity and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MS) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Dong Eun Kim, Seung Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 351. CrossRef - The Comparison between Periodontal Health Status and the Findings of Hypertension and Diabetes Disease of some Workers
In-Young Ku, Seon-Jeong Moon, Kyung-Hwan Ka, Myeong-Seon Lee
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(2): 81. CrossRef - The Relationship between Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adult Males and the Parents' Family History of Diabetes
Hyung-Su Park, Jin-Gyu Jeong, Jin-Ho Yu
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(5): 779. CrossRef - Associations of serum fetuin-A levels with insulin resistance and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
Chan-Hee Jung, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Sang-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2013; 10(5): 459. CrossRef - Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome
Sa Rah Lee, Ying Han, Ja Won Kim, Ja Young Park, Ji Min Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Mi-Kyoung Park, Hye-Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 357. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Therapeutic Target Achievement in Type 2 Diabetic Patients after Hyperglycemia, Hypertension, Dyslipidemia Management
Ah Young Kang, Su Kyung Park, So Young Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Ying Han, Sa Ra Lee, Sung Hwan Suh, Duk Kyu Kim, Mi Kyoung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 264. CrossRef - The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 374. CrossRef
- A Novel Clinical Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome: Vascular Risk Age
- A Case of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a GAD Antibody-positive Diabetes Patients who Recently Experienced Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State.
- Jang Won Son, Seok Hong Lee, Jung Ahn Lee, Jaetaek Kim, Yeon Sahng Oh, Soon Hyun Shinn
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(3):267-270. Published online May 1, 2005
- 975 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The term latent autoimmune diabetes in adults(LADA) was introduced to define adult diabetic patients who initially do not require insulin, but they have the immune markers of type 1 diabetes and in a number of cases, these patients progress to insulin dependency. LADA patients have several features of classic type 1 diabetes in addition to islet cell antibody positivity, including high rates of HLA-DR3 and DR4. We describe here a case of a patient with a diagnosis of LADA who, having been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, was affected with diabetic ketoacidosis. In April 2000, a 65-year-old man was admitted to Chung-Ang University Hospital due to his decreased cognitive ability. The patient was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes 30-years ago and he was diagnosed 6-month ago as being in a hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. He was positive for antibodies against GAD(anti-GAD, 31U/mL). His weight was 70kg, height 167cm, BMI 25 kg/m2 and the blood pressure was 86/52mmHg. No abnormalities on the physical examination were found. His acid-base balance was pH 6.937, serum bicarbonate 2.2mmol/L and the anion gap 38; he also had a strong positive reaction for ketones in his urine and serum. During half a year, the fasting C-peptide level decreased from 0.65nmol/L to 0.13nmol/L, which means the rapid progression of beta-cell destruction. Intensive treatment of LADA with insulin may improve this type of patients' quality of life, and so potentially save the beta-cell function and perhaps lessening the risk of a hyperglycemic crisis
- Study on the Methylglyoxal-induced Apoptosis in Bovine Retinal Pericytes.
- Jaetaek Kim, Seok Hong Lee, Jang Won Son, Jeong An Lee, Yeon Sahng Oh, Soon Hyun Shinn
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(3):199-207. Published online June 1, 2004
- 817 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
One of the histopathological hallmarks of early diabetic retinopathy is the loss of pericytes. Evidences suggest that this pericyte loss in vivo is mediated by apoptosis. However, the underlying cause of pericyte apoptosis is not fully understood. This study investigated the influence of methylglyoxal(MGO), a reactive alpha-dicarbonyl compound of glucose metabolism, on the apoptotic cell death in retinal pericytes. METHODS: Primary cultures of retinal pericytes were prepared from isolated bovine retinal microvessels. The cells were incubated under normoglycemic conditions after treatment with 200-800muM methylglyoxal for 6 hours. The cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay. The apoptosis and intracellular reactive oxygen species(ROS) generation were measured using an ELISA kit and flow cytometry, respectively. The NF-kappaB activation was detected by immunocytochemistry. RESULTS: MGO produced a progressive cytotoxic effect on the retinal pericytes. An analysis of the internucleosomal DNA fragmentation by ELISA showed that MGO(200 to 800muM) induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner. ROS were generated earlier and the antioxidant, N-acetyl cysteine, inhibited the MGO-induced apoptosis. The NF-kappaB activation and increased caspase-3 activity were detected. The apoptosis was also inhibited by the caspase-3 inhibitor, Z-DEVD-fmk, or the NF-kappaB inhibitor, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the elevated MGO levels observed in diabetes may cause apoptosis in the retinal pericytes through an oxidative stress mechanism, and suggests that the nuclear activation of NF-kappaB is involved in the apoptotic process.
- Role of Osmotic Stress in the Development of Chronic Diabetic Complications.
- Jaetaek Kim, Yeon Sahng Oh, Soon Hyun Shinn
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(3):160-163. Published online June 1, 2004
- 838 View
- 16 Download
- Methods of Research in Diabetic Retinopathy.
- Jaetaek Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(5):385-390. Published online October 1, 2003
- 776 View
- 16 Download

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





